Canadians are being pushed toward Electric Vehicles (EVs) as a step on the pathway to Net Zero.
An informed consumer is a smart consumer! Learn about EVs and use our EV Calculator to discover out how much you might save.
There are many makes and models of EVs on the market as well as a many that will be available in the near future. Many are listed Here
Key Things to Know about EVs
- Cold temperatures increase consumption when using heater, defroster, heated seats and built-in battery heating.
- Use of A/C during warm weather will increases consumption. This is offset to some degree as EV efficiency increases with temperature.
- Wet weather can increase consumption by a small amount due to the use of lights, wipers and possibly the defroster.
- As consumption increases, range decreases. Range in winter can be substantially less than in warmer weather. This can be a significant factor on long trips.
- As more people own EVs, the demand on the electrical grid will increase resulting in higher electricity prices and therefore operating costs
- As fewer people drive ICE vehicles, government revenue from gasoline sales (excise tax + road taxes) will decrease. This has already lead to EV fees being charged in many jurisdictions. These can be up to 1 1/2 times the taxes currently collected at the pump. It is a sure bet that Canada will follow suit.
- EVs are typically charged in the evening or over night. For the foreseeable future, renewables will be dedicated to base load on the grid. Therefore, the power to charge your EV will come from "Rolling Reserve" which is typically Coal and/or Nat Gas. This is true even when the majority of power is from hydro or nuclear as they do not respond to demand changes effectively.
EV Savings Calculator
Basic Facts about EVs:
- Advertised Range
- Range is the estimated distance you can drive on a full charge under Ideal Conditions
- Range is dependant on battery size, vehicle weight & performance characteristics
- Performance
- Acceleration (0 - 100 km/h) is one of the first things that many people look for. EVs in general offer very good off-the-line performance.
- Top speed is normally not important as all EVs can sustain highway speeds without trouble.
- Power & Torque are also important. Acceleration is great, but you want to ensure that the EV will also allow for safe highway passing.
- EVs come in rear, front and all-wheel drive. You choice should be dependant on normal road conditions in your area.
- Battery & Charging
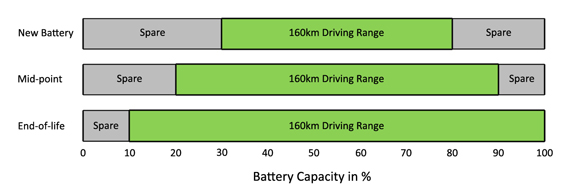
- Useable Battery capacity is important. EV batteries deteriorate over time. The way manufacturers mitigate this is by installing more battery capacity than what is needed when the vehicle is new. Over time, as the battery deteriorates, it's charging system will use more of the available capacity to maintain range.
- EVs normally have a built in charger, but it can vary in capacity. Typical charge times range up to 8 hours. A few EVs may be fitted with a fast charger, but this is not common at this time.
- Chargers are 90% - 95% efficient. Therefore, they will draw slightly more power than what is needed to charge the EV battery.
- External Fast Chargers can be installed in your home which will charge your EV at a faster rate (< 1 hr).
- Your home may not have the capacity to supply the amount of power required to charge your EV. This is not normally a problem with the built-in charger but may become an issue if you want need a fast charge. Check with a licensed electrician before purchasing your EV.
- Be aware that the move to "smart metering" may impact when and at what rate you can charge your EV. Smart meters allows the utility supplier to charge different rates during different times of the day or night. They can also have the capability to shut off your power if necessary as more people move to EVs and demand increases higher than the grid can handle.
- Energy Consumption
- Energy consumption is directly related to range.
- Manufactures will list an energy consumption rate (kwh/km) based on Ideal Conditions.
- A Vehicle Fuel Equivalent (liters/100 km) is also provided. This Should Not be used to compare directly to a Conventional Internal Combustion Vehicle. See our EV Savings Calculator.
- Climate & Weather
- Range and Energy Consumption provided by the Manufacturer and/or EPA are based on Ideal Conditions and do not translate perfectly to real world conditions.
- The Climate in your specific area plays a key role in determining your actual Range and Energy Consumption.
- Mild weather conditions (based on 23 C and no A/C use) will be similar to the rated range and consumption. Use of windshield wipers, lights, radio navigation, etc. will increase consumption to some degree. Use of A/C will significantly impact consumption.
- In Cold Weather, the use of heater, lights and windshield wipers will substantially increase consumption and reduce range. At temperatures below 0 C, a typical EV will see an increased energy consumption of 35% - 40% with a similar reduction in range.
- Because Li-ion batteries do not work well at colder temperatures, the EV will have a battery heater. When plugged in, this will consume additional energy and when not plugged in, the battery will supply the necessary power and range will be reduced.
- Due to the impacts of Cold Weather, it is advisable to have a garage to keep your vehicle in when not in use. If kept outside, it may be necessary to use the battery warmer to preheat the battery before using the EV.
- Real Consumption and Range
- As previously stated, power consumption and range ratings are for Ideal Conditions.
- The Climate specific to your area will impact your actual range and consumption.
- Driving habits will also impact consumption and range. It you tend to accelerate quickly and/or brake sharply, range will be reduced and energy consumption will increase.
- Other Costs
- An External Fast Charger can be installed in your home for faster charging. Typically cost is between $850 and $1200 and requires professionally installation. An electrical permit and electrical inspection may be required.
- As ICE vehicles become less numerous, the government will need to replace the revenue currently collected at the pump as Federal Excise Tax ($0.10/liter) and Provincial Road Taxes (up to $0.27/liter). Many governments are now charging a Yearly EV Fee. It is a safe assumption that Canada will not be any different.
Car & Driver Test Results - Impact of Cold Temperatures
Source
17% to 35% increase in energy consumption.

In Canada where winter temperatures reach -30 C, drop in performnce will be significant!
Go Back to the EV Savings Calculator